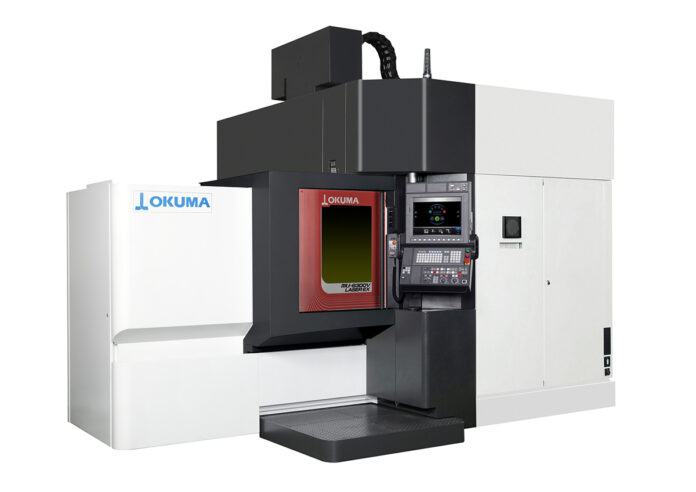
Okuma presented a new line of machine tools at the 28th Japan International Machine Tool Fair recently. The manufacturer’s trade innovations included state-of-the-art 5-axis vertical machining centres and a new type of intelligent multitasking machine. Among the highlights was the introduction of the world’s first multitasking machines capable of milling, turning, and grinding as well as laser-hardening and 3D metal printing.
Smart factory, just-in-time-production, varying order sizes – production and machining requirements are higher than ever. To meet those demands, Okuma’s latest machine tools take multitasking machining to the next level. The new models will be available in Europe in mid-2017.
Intelligent horizontal multitasking machine
To facilitate process-intensive production in a smart factory, Okuma has added the MULTUS U5000 to its line-up of multitasking machines. Designed for machining medium and large-sized components for the aerospace, energy and infrastructure industries, the MULTUS U5000 handles even difficult-to-cut materials, such as Titanium and Inconel. With the strongest turning spindle of its class, the MULTUS U5000 achieves unrivalled machining efficiency.
In an effort to allow operators to perform gear machining in-house, Okuma has made skiving and hobbing operations available on their multitasking machines with the accompanying software package enabling faster and easier programming.
With Industry 4.0 no longer a thing of the future, the MULTUS U5000 comes equipped with the latest generation of CNC control – OSP suite – as well as Okuma’s Intelligent Technology. These applications offer supreme connectivity and allow for a seamless integration of the machine tool into an Internet of Things – based production environment.
Smart Machine for 5-axis vertical machining
Designed to stand at the heart of a smart factory, Okuma’s latest 5-Axis vertical machining centre MU-S600V is able to instantly respond to changed lead-times and accommodates production formats ranging from high-mix, low volume to mass production.
The compact MU-S600V has a very small footprint with a machine-width of 1,400mm and is able to cut workpieces of up to 600mm in diameter. The machine’s compact dimensions and structural design allow for outstanding ease-of-use and easier crane jobs. Its robotic table enables completely unmanned, automated operations, eliminating manual handling of parts between set-ups in different machines. Production line layouts are easily adjusted in accordance with changes in production volume.
Laser technology for process-intensive machining
Designed to be the world’s first done-on-one – machines, the Okuma MU-6300V LASER EX and the MULTUS U3000 LASER EX are capable of milling, turning, grinding, 3D metal printing and heat treatment for a wide range of workpiece sizes and shapes. On-machine hardening provides the solution to a major bottleneck in production. Compared to hardening by conventional heat treatment, the process is quick and causes less distortion, resulting in dramatically increased throughput. The machine tools fully support agile manufacturing and process-intensive applications.
With a high-quality TRUMPF laser beam source at its core, Okuma’s LASER EX series enables stable laser processing over long runs. The machines allow for Laser Metal Deposition – LMD – for both large-capacity and high definition additive manufacturing. 0.4 to 8.5mm laser spot diameters enable unparalleled throughput regardless of the application. 3D moulding, coating and sectional repair of heat-resistant alloys and highly rigid materials are available on the machine as well.
Okuma’s OSP control meanwhile monitors and controls the entire process, ensuring reliable and stable additive manufacturing for products on par with forged components. The machine tools therefore meet the quality requirements of even the most demanding applications and industries such as aerospace machining.
Additional Okuma models with laser applications will be available shortly.
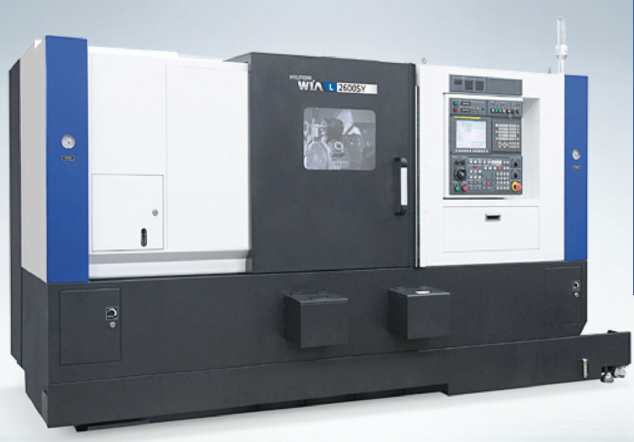




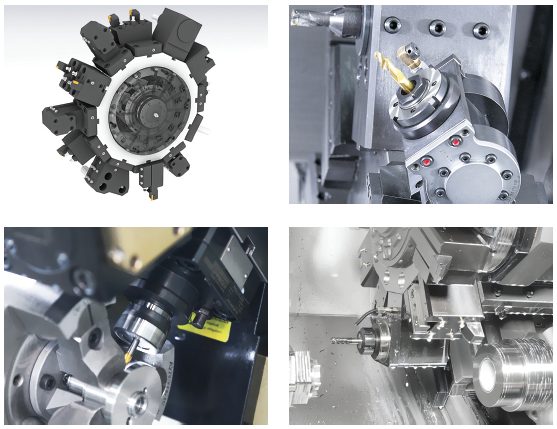 The L2600SY 12 station turret utilizes BMT65 tool blocks and can accommodate either static or rotary tools at each station. Rotary tool speed has been increased to 6,000 rpm, and turret indexing speed is a fast 0.15 seconds, station-to-station. Rapid positioning in the X and Z axis is performed at 1,181 inches/ minute, fastest in its class for a box guideway machine.
The L2600SY 12 station turret utilizes BMT65 tool blocks and can accommodate either static or rotary tools at each station. Rotary tool speed has been increased to 6,000 rpm, and turret indexing speed is a fast 0.15 seconds, station-to-station. Rapid positioning in the X and Z axis is performed at 1,181 inches/ minute, fastest in its class for a box guideway machine.